(DO NOT USE any of the compounds listed in this article without your doctor’s approval & supervision)
Inflammation is an inherent part of the healing process. It is actually a naturally occurring rapid immune response by which your body repairs damaged tissue, either from physical trauma, infection or allergy. Without it, injuries would never heal.
There are two types of inflammation: 1) Acute and 2) Chronic. The Second type can be broken down into two more sub-categories: 2a) Chronic Long Term Systemic Inflammation & 2b) Chronic Local Inflammation (i.e. muscle and/or ligament/tendon damage)
1) Acute inflammation is the response to a traumatic injury or infection (i.e. sprained ligament/tendon, strained muscle or to a pathenogen and/or virus – diarrhea, appendicitis). With respect to the latter, antibiotics are used to fight bacteria; much the same can be said about vaccines as they protect us from viruses. With respect to the former, other methods can be employed as shall be shown later on.7
The classic signs of acute inflammation are: heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function (See Figure 1). They are an immune response to healing. Normally, this process lasts for a few days or weeks (i.e. Chronic local inflammation).
Figure 1: The cardinal signs of inflammation — heat, redness, swelling, pain and loss of function.
2a) Chronic Long Term Systemic Inflammation is the presence of inflammation over an extended period of time
2b) Chronic Local Inflammation (i.e. muscle and/or ligament/tendon damage)
As with Acute inflammation, the classic signs as depicted in Figure 1, are also present here as well. Inflammation increases the movement of plasma and white blood cells from the blood into the injured area. This is when you would apply the acronym P.R.I.C.E. – and no not eat rice, but Pressure, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
The repair process begins with the coagulation phase, which lasts 1-2 days and is associated with lots of redness, heat (i.e. both as a result of increased blood flow to the damaged area) and/or pain.
Next, the inflammation phase follows, lasting up to 5 days post –injury. Immune cells (e.g. histamine, bradykinin, cytokines and pro-inflammatory prostaglandins) are called to the injured area, as a part of the healing process. The resulting tissue response to these compounds is fluid being released from the blood vessels, causing edema (i.e. swelling). This swelling brings with it, new nutrient and more immune compounds for the repair process.
The third phase, is the migration phase, which lasts from day 4 to 21 days post-injury.
Lastly, the remodeling phase lasts from day 5 up to 2 years post injury.
What are the Causes of Chronic Inflammation?
Usually there is a trigger mechanism malfunction at the cellular level i.e. by increased production of free radicals; adipose cells (production of inflammatory compounds – Tissue Necrcosis Factor (TNF) and others) cellular acidic toxins, elevated blood sugar levels, and oxidative stress. The release of these compounds causes damaging oxidative attacks on cellular proteins imbedded in membranes of cells and genes (i.e. your DNA). Left unchecked, overtime, these compounds contribute to the low-grade chronic inflammation, as mentioned earlier.8
Chronic Inflammation is often linked to poor diet – The typical Western Hemispherical diet (i.e. high in saturated fats, high omega-6 essential fatty acids, low omega-3 essential fatty acids, low in fruits & vegetables, high sugar and overcooked foods) which promotes a low-grade acidic condition in the body – known as whole body acidosis, which in turn is one of the largest contributors of inflammation. Other poor lifestyle factors can cumulatively contribute to inflammation. They are such factors as:
– Outdoor and indoor air pollution,
– Endocrine disruptors (i.e. xenoestrogens – from petrochemical products and other environmental toxins),
– Sleep deprivation,
– Artificial lighting,
– Chronic stress,
– Lack of exercise,
– Poor sleep habits,
– Low sex hormones,
– Smoking,
– Food-intolerances,
– Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) (a.k.a. electronic pollution)
– Obesity.
Instead of accelerating metabolism, chronic inflammation actually decreases it. Therefore, it is also sometimes called “Metabolic Dysfunction or Metabolic Syndrome.” The difference between Acute and Chronic is akin to the difference between a big bond fire vs. burning embers.6
In the not so very distant past, death rates were much higher due to poor living and working conditions (i.e. cities did not have sewers, fossil fuels, such as coal, were used, there was little running water, flushing toilets etc…), as a consequence infectious diseases were abound (i.e. Cholera, diphtheria, tuberculosis etc…) and life span was low) See Figure 2.
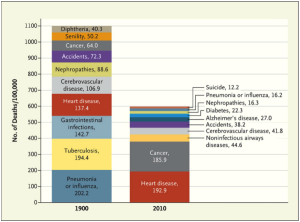 Figure 2: Top 10 causes of death: 1900 vs. 2010. Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
Figure 2: Top 10 causes of death: 1900 vs. 2010. Source: The New England Journal of Medicine
However, although the majority of us in the first world are no longer subject to what those individuals in the past underwent, we are now contending with Chronic Long Term Systemic Inflammation (a.k.a. “Cold Inflammation”). It has been linked to at least seven of the ten leading causes of death, ranging from accelerated ageing, weight gain, heart disease, cancer, neurodegenerative disease (i.e. Parkinson’s & Alzheimer’s), Type 2 diabetes, and kidney disease.
Chronic inflammation stimulates the production of 28 pro-inflammatory compounds from adipocytes (fat cells) and other metabolic cells (liver, brain, muscle) via the storage of toxins and excess cortisol. As a consequence, these inflammatory compounds begin to attack cellular membranes in different parts of the body, thus stimulating an Immune response (i.e. the release of inflammatory markers such as:
– Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF- α);
– Interleukin-6 (IL-6);
– C-reactive protein (CRP).
As more toxins are ingested, the fat cells become larger. The storage of this fat is usually centralized around the mid-section. It is known as Visceral Fat i.e. (the fat around your internal organs). Increased central obesity can be related back to chronic inflammation and disease, pro-inflammatory lifestyle factors such as stress, lack of sleep, and pollution can add to the mix.
The Solution
A well-structured, not too intense, weight training program and other dietary modifications can alter the release of the aforementioned pro-inflammatory compounds, including increases in a hormone called Leptin and interleukin-10 (IL-10 – an anti-inflammatory protein). Leptin has its role in appetite suppression.
The Problem With Inflammation
The normal inflammatory process should only last a few days, as the system is hard-wired to “turn off” at a certain point. The problem lies when the system does not “shut off”, and is left on for several months and even years, kind of like a “leaky faucet.” This is referred to as chronic inflammation, which can instigate further inflammation, much like a slow burning fire that is constantly being fed small amounts of kindling, which causes the release of inflammatory markers into the circulatory system. As these compounds begin to accumulate, they damage the healthy areas of the body. Hence causing tissue destruction in healthy non traumatized tissue such as (to name just a few):
– Joints and connective tissue (causing arthritis)
– Pancreatic tissue (causing diabetes)
– Blood vessel linings (causing hardening of the arteries)
– Intestinal lining (in gluten intolerance).
Anti-inflammatory Drugs May NOT BE the Answer For Some Individuals
Many medical practitioners prescribe over-the-counter and prescription drugs (i.e. prednisone, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) including ibuprofen and aspirin) for patients with inflammation. NSAID’s are used for the following reasons:
– They are among the most widely prescribed drugs for arthritis and other types of chronic and short-term inflammation
– They reduce inflammation through inhibiting production of both the pro- and anti-inflammatory prostaglandins
– They offer temporary, symptomatic relief from swelling, inflammation and accompanying pain
NSAID’s are not good for the following reasons:
– Anti-inflammatory drugs do not resolve the underlying issue
– They do not support the body in healing mechanisms
– Habitual use can result in possible unpleasant, and sometimes even dangerous, side effects (i.e. headaches, diarrhea, nausea to bleeding ulcers kidney damage and even cartilage damage)
– They can rob the body of many nutrients (i.e. vitamin C, calcium, folic acid, iron, potassium and pantothenic acid)
Natural Anti-inflammatory Products: The NATURAL ALTERNATIVES
Proteolytic (“Protein-Eating”) enzymes
– The vast majority of enzymes (3000+) found in the body regulate protein function at a cellular level
– There are some enzymes that are called proteolytic (e.g. Trypsin, Chymotrypsin)
– They regulate everything from liver function to the immune system and are known as proteases, or proteolytic enzymes
– They are important molecules produced continuously by the body especially in the area of the injury in order to reduce inflammatory chemicals, destroy dead cells, and activate new tissue growth
– They increase the breakdown of the fibrin, a fibrous protein partially responsible for blood clots and swelling during the inflammatory process
– With age, fibrin tends to build up in the body and contributes to a variety of conditions including slow wound healing, buildup of scar tissue, thickening of the blood, fibromyalgia, fibrous breasts, and uterine fibroid tumors
– Pain, edema, and the pressure within tissue can be eased when enzymes intervene, converting a chronic inflammatory condition into a regenerative healing process
– Proteolytic Enzymes are a safer alternative to the many prescription and over-the-counter pain relievers
– Proteolytic enzymes do not completely inhibit all phases of the inflammatory process [e.g. neutralizing bradykinins, induce the breakdown of fibrin – preventing excessive blood clots, digest dead tissue, cysts, scar tissue and arterial plaque, pain-blocking and anti-edemic (prevents swelling and fluid retention)], to a point where the body is unable to trigger the normal healing process
– Proteolytic enzyme supplements work by enhancing the normal function of our own proteolytic enzymes
– Proteolytic Enzymes are taken on an empty stomach & is easily absorbed from the intestinal tract
– Unlike NSAIDs, Proteolytic Enzymes have no inhibitory effects on the pro-inflammatory prostaglandins and are devoid of gastrointestinal side effects
– Systemic inflammation contributes to the development of arterial blockage
– Cardiac patients with high levels of CRP (C-reactive protein, a marker for systemic inflammation) can use Proteolytic Enzymes to combat inflammation
– Proteolytic Enzymes are a good blood-thinning agent, especially when combined with Fish Oils. Therefore, it is wise to consult your physician, especially if you’re already taking any form of anticoagulant therapy
– Proteolytic Enzymes have been used successfully for years as an anti-inflammatory agent in the treatment of chronic sinusitis (i.e. to improve the elimination of mucus from the bronchopulmonary airways), traumatic injury (e.g. sprains and torn ligaments), fibrocystic breast disease, post-operative inflammation and to facilitate the therapeutic effect of antibiotics in the treatment of infections (i.e. urinary bladder inflammation known as cystitis), sports injuries, arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, & PMS
Vitamin C
– Helps reduce cortisol production & can lower your levels of C-reactive protein (CRP)
– Helps with the formation of new collagen
– Suggested dose 1000mg/day to upwards of 4000 – 5000 mg/day (divided doses – short term use only)
– Use mineral ascorbate form vs. ascorbic acid
– Do not use cheap counterpart sodium ascorbate
– Check out “Liv-On”, “Prairie Naturals” “Ester-C”
Tumeric
– Used in Ayurvedic medicine
– Recommend for all inflammatory disorders, including arthritis, tendonitis, and autoimmune conditions
– Suggested dose take 400 to 600 milligrams of turmeric extracts (available in tablets or capsules) three times per day or as directed on the product label
– Whole turmeric is more effective than isolated curcumin, its major constituent
– Look for products standardized for 95% curcuminoids
– Full benefit takes two months to develop
– Don’t use turmeric if you have gallstones or bile duct dysfunction or are a Pregnant woman
– In rare cases, extended use can cause stomach upset or heartburn
– If you suffer from acne, turmeric is not only helpful taken internally but you can also use it externally by making a turmeric paste. Put on your face or other areas of the skin for 20 minutes or overnight to reduce inflammation and clear up a break out. Keep in mind this might turn your skin orange so don’t do this before a special event.
– Turmeric root can be juiced and used as a pain reliever
– Even chronic sufferers of arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can experience relief by using turmeric on a frequent basis
– Use it raw for best results by sprinkling it on salads and raw dishes as well as mixing it into fresh vegetable juices & coconut water (See Recipe)
Ingredients:
1-2 tsp. of Turmeric Powder
1oz raw ginger Root
1 cup coconut water and / or ½ cup Raw Pineapple
Mix into fresh vegetable juice made in with celery, cucumber, lemon
– Turmeric has high amounts of anti-oxidants that fight cancer causing free radicals, keeping your immune system strong
– If you have a cold or flu, turmeric is one of the best things you can do to speed up recovery
– This is a very cleansing mixture, as a result you may need to use the washroom frequently, but this is normal
– Even chronic skin conditions like psoriasis can be helped with turmeric
– For a healthy skin regimen, make turmeric cocktail every day for 2 weeks accompanied by fresh raw foods, juices and green smoothies.
– Turmeric also contains good amounts of iron and other minerals so use it as a blood builder
Oregano Oil
– Organic oregano oil is rich in carvacrol, flavonoids, terpenes, (i.e. used as decongestants and histamine reducing agents), and rosmarinic acid and research reveals that rosmarinic acid inhibits allergy-related inflammation (i.e. reduces fluid buildup and swelling)
– Helps to address pollen, dust, mold, chemicals, fungus and bacteria entering the body and causing a histamine reaction (i.e. symptoms such as nasal congestion, increased mucous production and sneezing)
– Strengthening the immune system
– Oregano oil also contains organisms that create skin infections and digestive disorders
– Helps develop better joint and muscle flexibility
– Can improve respiratory health
– Look for oregano oil that does not contain alcohol
– Find a brand with at least 80% carvacrol
– Purchase only Oreganum Vulgare (a.k.a. “wild” oregano)
– Use a low dose at first like 3 drops in water or under the tongue twice daily. Increase to 6 drops twice a day – which is considered a therapeutic dose.
– Some people report feeling a burning sensation in the mouth, but this will dissipate after a few seconds
– Good brands: “Wild Oil of Oregano by Hedd Wyn” (has highest potency & this company only specializes in Oregano Oil). We have tried others, but found this brand to be the best in terms of quality of product & value for your dollar)
Ginger
– Used in Ayurvedic medicine
– Powdered dry ginger is an excellent anti-inflammatory
– Take one to two capsules (500 to 1000mg) twice a day with food
– You won’t get the full effect for two months
Garlic
– It is anti-inflammatory
– Helps to increase white blood cells (macrophages)
– Dosage: 2-4 garlic cloves each day or 600 to 1200 mg of aged garlic extract
Pineapple
– Contains Bromelain, which is anti-inflammatory
– Dosage: 2 cups of pineapple per day or 2000-6000 micro units taken on empty stomach
Hops
– The flowers of “Humulus lupulus,” (i.e. hops) are a essential ingredient in beer
– Used by practitioners of herbal medicine for their sedative and antibacterial properties
– Contain phytoestrogens, which are compounds that mimic the effects of estrogens in your body
– Has immune-modulating (i.e. the alpha- and beta-acids from hops appear to block the release of inflammatory chemicals called cytokines from white blood cells)
– Enzymes called cyclooxygenases largely regulate the inflammatory processes in your body. Cyclooxygenase-1, or COX-1, and cyclooxygenase-2, or COX-2, convert fatty acids to compounds called prostanoids, many of which are responsible for causing inflammation in your tissues
– The therapeutic effects of commonly prescribed anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or celecoxib, are due to inhibition of COX enzymes
– Hops extract selectively inhibits COX-2 in a manner similar to the prescription medication celecoxib
– Hops contain chalcones and other polyphenols, which are similar to the catechins in green tea.
– Xanthohumol, one of the primary chalcones in hops, inhibits the activity of human hepatic stellate cells — the primary instigators of inflammation and scarring in liver disease
– Can possibly reduce inflammation in animal models on nonalcoholic steatosis, a.k.a. fatty liver disease
– Hops exert a minor anti-tumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in animal studies and in tissue cultures of human cells.
Rose-Hip
– Is an anti-inflammatory
– Rose-hip extract reduced chemotaxis of peripheral blood neutrophils and monocytes
– Rose-hip can minimize the discomfort from osteoarthritis, resulted in reduced serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and reduced chemotaxis of peripheral blood neutrophils
– Rose-hip contains a high amount of vitamin C
Cayenne Pepper
– Originated in tropical South America, and is now grown all over the world
– It is a well-known member of the capsicum family of plants
– This family includes the red bell peppers, which are commonly used in cooking, paprika often sold as a spice, and the hot peppers known as cayenne peppers
– All members of the capsicum family including cayenne contain the active ingredient called capsaicin, which is the part that tastes hot and spicy
– Capsaicin is the active ingredient in a cayenne cream called Zostrix, used as a painkiller for many types of arthritis including gout
– You do need to take care when you are using the cream, and make sure you wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after using it, as it can cause severe pain if you get it in your eyes or your mouth
– Capsaicin is a counter irritant (i.e. this refers to the way that it irritates the skin, and when this happens this uses up all of the pain messengers in the area. It also enters the nerve and gets rid of a substance there that is causing your pain)
– Is a potent inhibitor of substance P (i.e. a neuropeptide associated with inflammatory process)
Papaya
– Contains Papain, which is anti-inflammatory
– Dosage: 1 to 1 ½ cups per day or 500-1000mg in supplemental form
Boswellia
– It is the extract of the herb Boswellia
– Used in Ayurvedic medicine and available in capsule form
– It may be useful for generalized inflammatory conditions such as fibromyalgia
– The dosage is 400mg x 3 / Day
Malic Acid
– 1200 to 2400 mg divided into x 3 / Day
Magnesium Citrate / Aspartate / Malate
– 200 to 600 mg divided into x 3 / Day
Evening Primrose Oil (GLA)
– Anti-inflammatory
– 500mg to 200mg divided into x 3 / Day
Methlysulfonymethane (MSM)
– Anti-inflammatory
– 1 to 2 g divided into x 3 / Day
Omega-6 fatty acids & Omega-3 fatty acids
– These compounds are sourced only from fats
– Ideally, you should have an even ratio of both so that your body can shut down the inflammatory process effectively
– The average, North American diet contains a ratio of 17:1 pro-inflammatory (i.e. Omega-6) to anti-inflammatory fats (i.e. Omega-3)
– A good ratio is about two or three omega-3 fats to every omega-6 fat consumed
Omega-6 fatty acids
– Are responsible for pro-inflammatory compounds
– Come from saturated fat sources: Butter, Red Meat
Omega-3 fatty acids
– Are responsible for anti-inflammatory compounds
– Sources: Sardines, Mackerel, Wild Salmon, Chia Seeds, Walnuts, Olives, Almonds, Mixed Nuts, Avocados, Flax Seeds
– Omega-3 supplements are NOT all created equal
– Do not just purchase any random bottle from big name food / warehouse stores
– They should be packaged in a dark, light free, sealed bottle away from heat, light and oxygen
– You want Molecularly Distilled wild salmon and/or wild sardines and mackerel, not a farm fish source
– Good brands are: Carlson, Metagenics, Ascenta
– Dosage: 3-9 grams of fish per day.
Homeopathics Can Possibly “Cut healing time by ½ or greater”
Arnica Montana
– Helps manage bruising *
– Helps to reduce swelling
– Promotes healing
– Eases pain
– Can be used to prevent Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) by taking a couple of pellets before the event
– You need to match the severity of the injury with the strength of the homeopathic medicine (i.e. lower potency for smaller trauma & vice versa)
– Topical Arnica cream can be applied topically to the traumatized area to further aid in healing
– A popular topical cream is “Traumeel” by Heel or others can do as well
* What is a bruise?
– Bruises are what medical doctors call “contusions”
– They occur when you get injured and break tiny blood vessels in the skin. These blood vessels or capillaries, leak into the surrounding tissue and as red blood cells gather, you can see discoloration in the area
– It starts off as a red-purple injury becomes green or yellow as the body works to heal the region and metabolize the mass of escaped red blood cells
– The degree and how easily a person bruises varies from one person to another
– Older people (vs. younger children) have more delicate vessels
– Some Medications prevent blood clotting (i.e. Coumadin)
– Some Medications, like Prednisone, make blood vessels more fragile and thus often contribute to increased bruising
– Most bruises heal after 2 to 3 weeks (i.e. the skin color returned to normal)
– On occasion the body will wall off the region instead of sending cells in to do the clean up work due the pooling of blood in the area of the bruise
– If the bruise is very deep (i.e. to the depth of the bone), calcium is released from the damage muscle and is deposited into the surrounding tissue space between the muscle and the bone creating a condition called myositis ossificans (a.k.a. “Charlie horse”)
Rhus Tox
– Nicknamed the ‘rusty gate’ remedy
– Effective for joints that are stiff from injury or overexertion
– It is particularly useful when muscles or joints are worse first thing in the morning, with cold, damp weather, but feel better after gentle motion and with warm applications
Bryonia
– Nicknamed ‘The Grumpy Bear’ remedy because it helps people who do not want to be bothered
– It is used for symptoms of pain that worsens with the slightest movement
– Derived from wild hops
– Relieves pain that is ameliorated by pressure, or by lying on the painful side
Calc Phos 6x
– Aids many conditions involving structural stress and growth
– Derived from a mineral containing phosphorous and calcium, primary constituents in bone
– Plays an important role in bone repair after fractures (non-union) and during grown periods
Hyperpicum Perforatum 6x HPUS
– Weakness in limbs
– Joint pain
Ruta Graveolens 6x HPUS
– Pain in limbs, joints & bones
Ledum Pal 6x HPUS
– Swelling; aches & pains
– Inflammation
Bellis Perennis 6x HPUS
– Muscular soreness; fatigue; sprains
OTHER NOTABLE METHODS & COMPOUNDS
– Take it easy during the first 12-48 hours. Sore muscles don’t have full function, and continued strenuous demands carry a heightened risk of injury
– Hot bath with 2 cups Epsom salts + 2 cups Baking Soda + ½ cup Apple Cider Vinegar + 20 drops Lavender (soak for 15 to 20 min.)
The caveat: avoid excess heat for two to three hours after a tough workout, as it will promote circulation and increase inflammation.
– Kneading + Jostling Massage can help ease sore stiff muscles
– Fluid intake flushes excess acids from your body, and supplies it with important minerals. Good choices include herbal teas and vegetables and/or fruit juices diluted with mineral water containing little or no sodium
– Rubs containing extracts of menthol, camphor, St. John’s wort, eucalyptus, spruce needle, thyme and horse chestnut can be added to a massage
– The lack of minerals such as magnesium, potassium, and calcium is probably the biggest cause of nighttime leg cramps, they are abundant in fennel, broccoli, bananas, dried fruits, oatmeal, nuts, milk, and cheese.
– Cider vinegar provides your body with potassium; drink 1 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in 1 cup of water every evening for 2 to 4 weeks
– If your cramps are the result of a magnesium deficiency, taking magnesium in the form of effervescent tablets, in consultation with a doctor, might help
– Use adhesive compress like “SALONPAS” to provide constant warmth and essential oils to an injured area (best used once the swelling has gone down, but there is still pain and tissue repair in not complete)
– You can also take dietary steps to reduce inflammation via specific fats in your diet that affect the way the body makes prostaglandins (i.e. a group of hormones that regulate inflammation)
– Some prostaglandins intensify the inflammatory response while others reduce it
– To help your body reduce inflammation eliminate polyunsaturated vegetable oils, margarine, vegetable shortening, all partially hydrogenated oils and all foods that contain trans-fatty acids (read food labels to check for the presence of these oils)
– Use the Essential Oil Lavender. It has some very good anti-inflammatory properties. “Plus you’ll smell a whole lot better.”
– Avoid Excitotoxins as these substances over stimulate the neurons and in excess can lead to neurotoxicity. Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is the sodium salt of the amino acid glutamic acid or glutamate and is used to enhance the flavor of food. Aspartame is a dipeptide of aspartate and phenylalanine used in foods, beverages and Prescription Meds. Aspartame has been linked to headaches, seizures, dizziness, movement disorders, angioedema and anaphylaxis



